The SEO industry in the US is worth over 20 billion dollars, with countless websites vying for top spots on online search results. Search engine optimization (SEO) refers to a set of practices to match webpage characteristics to the ranking criteria used by top search engines. Strategic SEO techniques can help websites garner online visibility and attract organic traffic without relying on ads. Hence, organizations must adopt SEO best practices to consolidate their digital presence and grow their reach. While countless factors impact SEO, a Robots.txt file is one of the lesser-known concepts to increase your SEO score!
Robots.txt File: What Does it Mean?
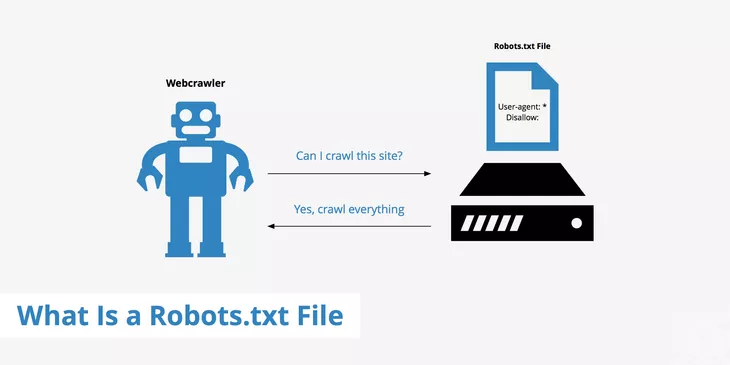
A Robots.txt file is a simple text file, typically located in the root directory of your website, that communicates with search engine crawlers. It acts as a set of instructions, guiding these crawlers on which parts of your site to crawl and which to avoid. A crawler is a search engine robot that collects data from websites across the internet and adds the information to its databank.
(Image Source = https://seosherpa.com/robots-txt/)
Proper crawling and indexing are crucial for SEO, as they can help your site content gain visibility on the search results. However, in certain cases, you may want to restrict the crawler from accessing specific URLs. In those cases, using the Robots.txt file can help. This file allows or disallows the crawling of specified pages, and most top search engine crawlers respect these instructions.
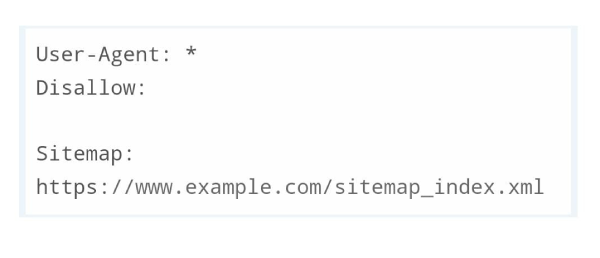
Example of a simple robots.txt file.
(Image Source = https://www.hostinger.in/tutorials/wordpress-robots-txt?ppc_campaign=google_search_generic_hosting_all&bidkw=defaultkeyword&lo=1007828&gclid =Cj wKCAjwvdajBhBEEiwAeMh1Ux0iBw-A3QNod6vMqpmPsCq8WWSikUGJPkpEF157Fwiq8L4Ka5k9NxoCfpsQAvD_BwE)
How Do Search Engine Crawlers Interact with Robots.txt Files?
Crawlers from search engines like Google crawl the world wide web to identify information. They index this data so that the search engine can display this web content in response to search queries from users. These crawlers, also known as spiders, visit billions of URLs to crawl and index data. However, before a crawler starts collecting data, it looks for a Robots.txt file in the top-level directory. If it is present, the crawler checks the file and refrains from crawling the disallowed pages. However, in the absence of this file, it crawls all the pages on the site.
Robots.txt File Syntax:
The syntax of the robots.txt file follows a specific format. Here’s a description of the syntax elements:
1. User-agent
This directive specifies the web robot to which the subsequent rules apply. Multiple User-agent directives can be used to define rules for different robots.
2. Disallow
This directive specifies the paths or files that should not be crawled or indexed by the specified user-agent. It defines the parts of the website that should be off-limits to the robot. You can specify individual files or directories.
For example:
User-agent: * Disallow: /private/ Disallow: /temp/file.html
3. Allow
This directive specifies exceptions to the Disallow directive. It indicates the paths or files that are allowed to be accessed by the specified user-agent. It is used to override more general rules.
For example:
User-agent: Googlebot Disallow: /private/ Allow: /private/public.html
4. Sitemap
This directive specifies the location of the website’s XML sitemap file. It provides a URL to the sitemap that contains a list of all the pages on the site.
For example:
Sitemap: https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml
5. Crawl-delay
This directive specifies the time delay (in seconds) that a robot should wait between successive requests to the website. It is used to prevent excessive server load.
User-agent: * Crawl-delay: 5
6. Comments
Lines starting with “#” or “//” are considered comments and are ignored by web robots. You can use comments to provide additional information or explanations within the robots.txt file.
Here’s an example of a basic robots.txt file:
User-agent: * Disallow: /private/ Disallow: /admin/ Allow: /public/ Sitemap: https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml
In this example:
- The User-agent directive * applies to all robots.
- The Disallow directive /private/ instructs all robots not to crawl the /private/ directory.
- The Disallow directive /admin/ instructs all robots not to crawl the /admin/ directory.
- The Allow directive /public/ allows all robots to crawl the /public/ directory, even though it’s disallowed by default.
- The Sitemap directive specifies the location of the XML sitemap file for the website.
You can also specify rules for specific user agents. Here’s an example:
User-agent: Googlebot Disallow: /private/ Allow: /public/ User-agent: Bingbot Disallow: /
In this example:
- The first set of rules applies to the Googlebot user agent.
- The Disallow directive /private/ instructs Googlebot not to crawl the /private/ directory.
- The Allow directive /public/ allows Googlebot to crawl the /public/ directory.
- The second set of rules applies to the Bingbot user agent.
- The Disallow directive / instructs Bingbot not to crawl any part of the website.
When Should You Use Robots.txt Files to Restrict URLs?
You can strategically use the Robots.txt file to restrict parts of your website. The following are some common reasons why site owners use this file type to disallow access:
-
Preventing Duplicate Content
Robots.txt allows you to avoid duplicate content issues. Search engines penalize websites with duplicate content because it hampers user experience and dilutes the search results. By disallowing access to duplicate content through the Robots.txt file, you can avoid such penalties and ensure that search engines prioritize the fresh and unique content on your site.
-
Blocking Private Pages
Often, sites have pages that are necessary but not appropriate for indexing. For example, you may not want users to visit your site’s staging page. You may also want to block an internal search results page from Google’s SERP. In such cases, you can disallow crawling with a Robots.txt file.
-
Restricting Resource Files
You may not want images, videos, and PDFs on your site to show up on the search results. In those cases, you can use a Robots.txt file to disallow access. This step can also help you better manage the crawl budget.
-
Managing Crawl Budget
-
Specifying the Sitemap
The Robots.txt file can guide search engines to your sitemap. Including a reference to your sitemap in the Robots.txt file ensures that search engine crawlers discover and index all the critical pages on your website. As a result, it helps improve the visibility of your content in search results and boosts your overall SEO efforts.
A Robots.txt file helps manage the crawl budget. Search engine crawlers have limited resources, allocating a specific amount of time to crawl each website. By instructing them to skip certain sections or files, you can ensure that they focus on crawling the most crucial and relevant pages. This step often maximizes the efficiency of the crawling process.
When Should You Not Use a Robots.txt File?
While the Robots.txt file can be very useful to block access to certain pages, you should know when to use it correctly. You should not use this file type to hide sensitive or confidential information from search engines. If other pages on your site have descriptive text pointing toward those pages, the crawlers may index the information from visiting the restricted URLs. For private and confidential pages, it is better to use password protection or the “noindex” directive.
Link Between SEO and Robots.txt Files
Creating and adding the Robots.txt file can help you optimize your site more efficiently. As a result, you can potentially improve your SEO score and increase your chances of ranking higher on the Google SERP. By establishing the necessary guidelines for crawling your website, a Robots.txt file can help with the indexing process that forms one of the foundational aspects of SEO. The following are some best practices you can follow while using a Robots.txt file to optimize your site for search engines:
- Carefully review your Robots.txt file to ensure you do not disallow access to any webpage you want the spider to index.

Example of a directive such as “disallow” in the robots.txt file
(Image Source = https://www.hostinger.in/tutorials/wordpress-robots-txt?ppc_campaign=google_search_generic_hosting_all&bidkw=defaultkeyword&lo=1007828 &gclid=CjwKCAjwvdajBhBEEiwAeMh1Ux0iBw-A3QNod6vMqpmPsCq8WWSikUGJPkpEF157Fwiq8L4Ka5k9NxoCfpsQAvD_BwE) - You can customize the instructions in your Robots.txt file to ensure that various user agents from the same search engines can crawl and index suitable parts of your site. For example, Google uses different agents for organic and image searches, and you can fine-tune your Robots.txt file to reflect the same.
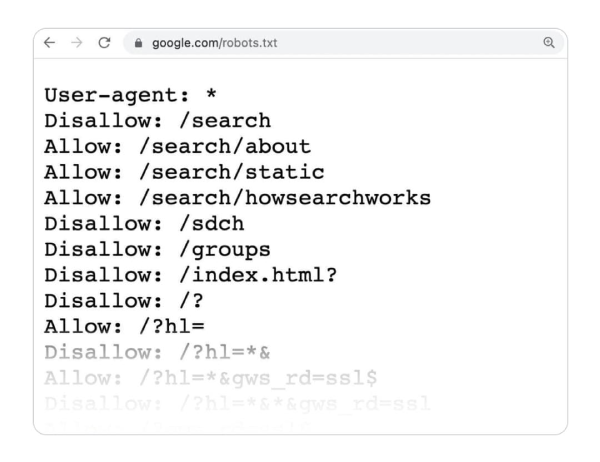
Syntax of “allow” and “disallow” directives.
(Image Source = https://yoast.com/ultimate-guide-robots-txt/) - You can submit your Robots.txt file to Google to ensure it considers the latest updates. Usually, the bot creates a cache of the Robots.txt file, updating it once a day. However, you can submit the file for urgent updates.
In the world of SEO, the Robots.txt file acts as a gatekeeper, regulating how search engine crawlers interact with your website. By leveraging the power of the Robots.txt file, you can enhance your website’s SEO performance. Professionals from a reliable SEO agency can help you perfect these technical elements to boost your SEO score and drive organic traffic. Contact the Forix SEO team today to get started with acing your SEO!
Let Us Get the Results You Want
The key to outranking competitors and reaching the top spots in Google really comes down to a comprehensive SEO strategy and a tremendous amount of effort. We have found a way to package both – simplifying SEO for our clients. Our team of experienced SEO professionals can help you achieve the outcomes you want at a reasonable price.