Just like Hogwarts and God’s plan, search engines work in mysterious ways. Yes, you heard that right!
When you publish new content, Google indexes it for users to find it in the search results as fast as possible. Once you are out of square one and get some new SEO experience under your belt, you probably think indexability and crawl budgets are the beginner’s game, until they are not!
One day you upload your content and search engines don’t index it. You scratch your head; try every other way to rank the content or at least make Google index it, but indexing doesn’t feel like a cakewalk anymore.
Indexability issues can sink your site traffic and make all your SEO efforts go in vain. Fortunately, there are several tips and tricks in our SEO toolbox to help your website indexing. Sit back, grab your reading glasses and let the indexing secrets unfold one step at a time!
#1 Create and Submit an XML Sitemap
A sitemap is like a treasure map for SERPs to crawl your site and index the web pages efficiently. So, an XML site map contains a list of all the pages on your site and by creating a comprehensive sitemap and submitting it to Google Search Console, you provide a clear roadmap for search engine bots to navigate your site. Use a sitemap generator to create an XML version or tag the canonical version of each page with duplicate content to manually create one in Google Search Engine Console.
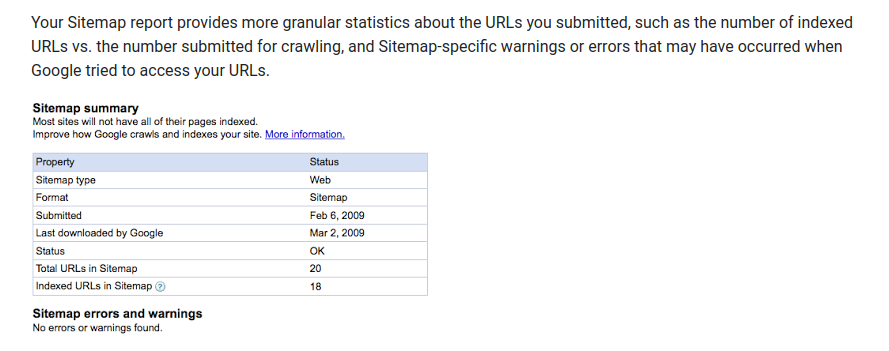
Source: https://developers.google.com/search/blog/2009/03/using-stats-from-site-and-sitemap
#2 Use Google Search Console to Track the Crawl Status
You can always use the Google Search Console to track the crawl status in order to identify any potential issues or errors that may hinder the website indexing process. This information allows you to take prompt action to resolve crawl errors, broken links, or any other factors that may negatively impact indexing. From 404 and DNS errors to server errors and Robot.txt errors, tracking the crawl status can help you to find out underlying issues including failed connection, timeout, no response, etc.
#3 Optimize Robots.txt File
A robots.txt file is a basic text document that outlines guidelines regarding the accessibility of specific sections of a website by web crawlers. For instance, a robots.txt file might look like this:
# This robots.txt file controls crawling of URLs under https://example.com. # All crawlers are disallowed to crawl files in the "includes" directory, such # as .css, .js, but Google needs them for rendering, so Googlebot is allowed # to crawl them. User-agent: * Disallow: /includes/ User-agent: Googlebot Allow: /includes/ Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap.xml
Source: https://developers.google.com/search/docs/crawling-indexing/robots/robots_txt
The robots.txt file tells search engine crawlers which parts of your website should be crawled and indexed and which ones should be excluded. Verify that important pages and content are accessible to search engine bots, while private or duplicate content is appropriately blocked. Use the “Disallow” directive to block specific pages or directories that you don’t want to be indexed.
#4 Enhance Website Speed and Performance
According to a recent survey by Pingdom, sites that load in 1second have a 7% bounce rate, that load in 3 seconds have an 11% bounce rate and the ones with five second turnaround time have a 38% bounce rate. User attention spans switch in seconds and just like regular people, Google prioritizes websites that offer excellent user experience. Slow-loading or buffering pages can hinder website indexing and negatively impact your search rankings. Optimize your website’s speed by minifying CSS and JavaScript files, compressing images, leveraging browser caching, and selecting a trustworthy hosting company.
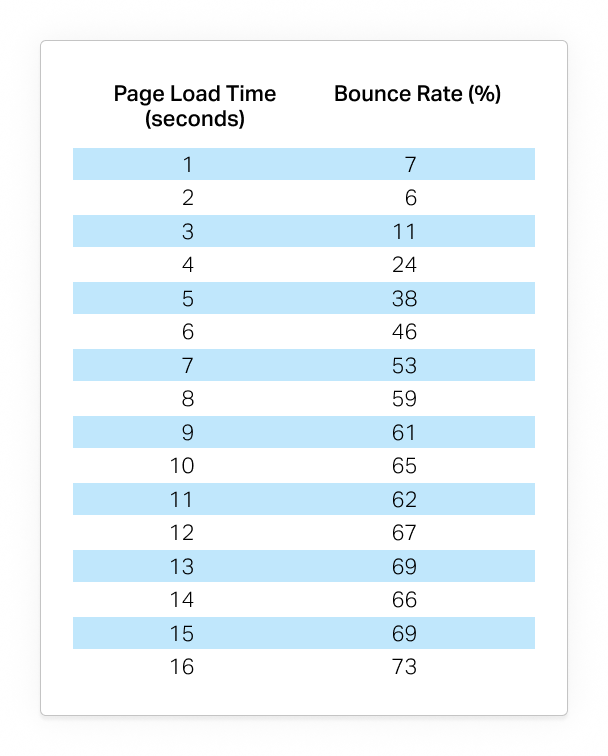
Source: https://www.pingdom.com/blog/page-load-time-really-affect-bounce-rate/
#5 Use Canonical Tags
Duplicate content can confuse search engines and dilute the website indexing process. Implementing canonical tags helps indicate the preferred version of a webpage to search engines. It consolidates duplicate content into a single, authoritative source, preventing indexing issues caused by multiple pages with similar content.
#6 Improve URL Structure
A clean and organized URL structure aids search engines in understanding the content and relevance of your web pages. Incorporate relevant keywords and descriptive phrases into your URLs, making them user-friendly and search engine-friendly. Avoid lengthy URLs with unnecessary parameters, as they can mislead search engine crawlers and affect indexing efficiency.
#7 Optimize Metadata
Well-optimized metadata doesn’t just help with your website indexing, it also enhances the click-through rate (CTR) of your pages. Metadata, such as meta titles and meta descriptions, provides essential information about your web pages to search engines and users. Craft compelling and concise meta titles that include relevant keywords, accurately representing the page’s content. Similarly, write unique meta descriptions that entice users to click through from search results.
#8 Relevant, Relatable, Reliable High-quality Content
High-quality content is the cornerstone of any successful SEO strategy and website indexing is no different. Creating compelling content that sells less and helps more. Provide valuable information, solve problems, engage your target audience and be consistent in your content marketing efforts to signal search engines that your website is active and worth indexing.
#9 Optimize Internal Linking
Anyone who is a pro in the SEO game understands how strategic internal linking enhances site structure, user navigation and indexing efficiency. Internal links are hyperlinks that connect one page of your website to another. They help search engine crawlers discover and index additional pages on your site, improving the overall indexing process. Incorporate relevant anchor texts when linking internally, and use descriptive keywords that provide context about the linked page’s content.
#10 Google Indexing API
Search engines care about SEO professions as much as SEO experts care about search engines. Within the past few years, both Google and Bing have rolled out new APIs to help speed up and automate the indexing and crawling of URLs. You can use these APIs as well as they allow for immensely speeding up indexing by submitting more than 100s or 1000s of URLs.
Conclusion
Remember, SEO is no do-it and forget-it process, it is a long-term approach. If you want your website indexing and crawlability issues to vanish, staying current with the industry-leading SEO practices is vital before things get out of hand and start affecting your rankings. Whether it is AI-generated content or Google algorithm updates, search engines work in disruptive landscapes. If you are not sure about website indexation, run a quick scan in the Google Search Console to find out how you are doing because the results can be certainly educational.
Still, need more information on how to index your website on Google or want help to index a website? Contact our team of professionals at Forix now!
Let Us Get the Results You Want
The key to outranking competitors and reaching the top spots in Google really comes down to a comprehensive SEO strategy and a tremendous amount of effort. We have found a way to package both – simplifying SEO for our clients. Our team of experienced SEO professionals can help you achieve the outcomes you want at a reasonable price.
